|
This tutorial you will build one or more digital temperature gauges linked to your Raspberry Pi that can be viewed on the WWW or your smart phone.
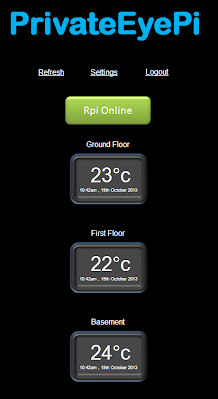
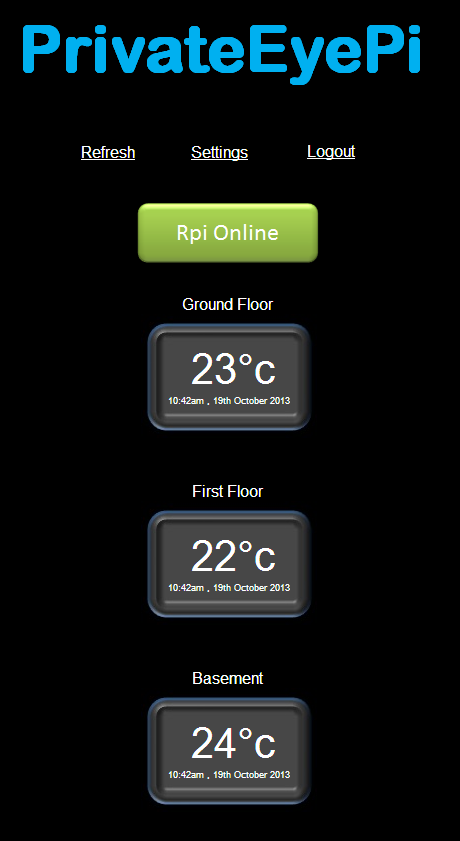
At the end of the project you will have a WWW dashboard that looks similar to this:
What you need:
For support, queries or suggestions please visit our support forum.
Step 1: Build and test the Electronics:
Parts can be purchased from our store: https://www.jemrf.com
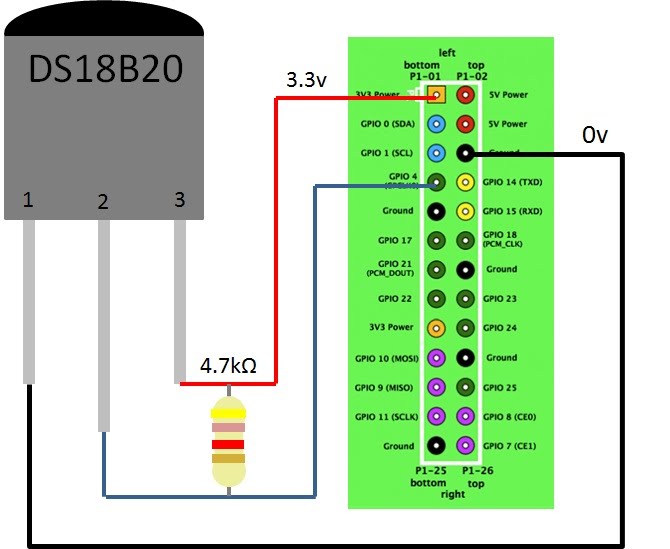
Figure 1. DS18B20 temperature sensor circuit diagram
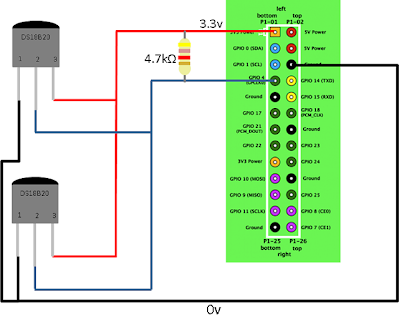
If you want to add multiple sensors daisy chain the middle pin of the sensors. This will work because every DS18B20 sensor has a unique ID that is used to differentiate the signals coming from the sensors See Figure 2 below.
Figure 2. Multiple DS18B20 temperature sensor circuit diagram
Once built, follow the following steps to test that it is working:
Log in to your Raspberry Pi
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Page down to the bottom of the file and paste or type in these two lines (if they are not already in the file).
# 1-wire settings
dtoverlay=w1-gpio,gpiopin=4
Press CTRL-X Y ENTER to save exit.
Reboot your Pi
Then enter the following commands to get a reading from the DS18B20 sensor:
sudo modprobe w1-gpio
sudo modprobe w1-therm cd /sys/bus/w1/devices/ ls
You will see a listing of the current directory. There should be a directory that is the serial number of your temperature gauge. The serial number of my thermometer 28-0000040be5b6, but every one will be unique. Make a note of yours as you will need it later in step 4. If you have multiple sensors there will be multiple directories listed.
If you don't see a directory with lots of numbers and letters like the one above then:
If you do see the directory then type cd followed by the directory name:
cd 28-0000040be5b6
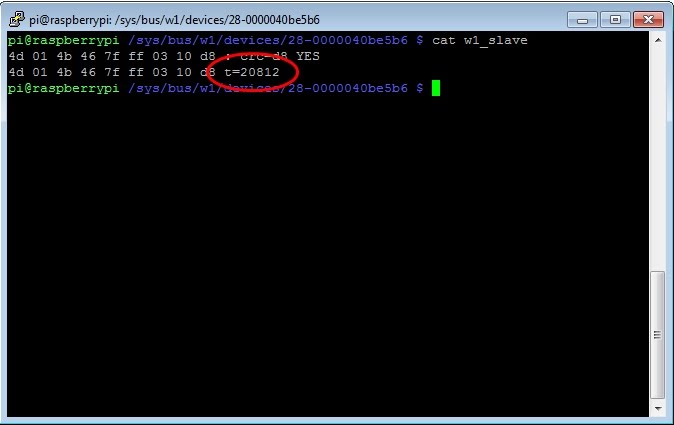
cat w1_slave
You will now see a dump of the w1_slave file that contains the temperature data in celcius (refer Figure 3). 20812 is 20.812 degrees celcius. The dashboard does support a Fahrenheit setting that we will cover later if that is your preference.
Step 2: Register an account with PrivateEyePi
If you have not yet registered with PrivateEyePi follow the following steps, otherwise proceed to Step 3. Note this is a completely free service and has no trial period.
Step 3: Install/Upgrade your PrivateEyePi software
Follow the following link to the tutorial -> Install PrivateEyePi Software
Step 4: Configure the program
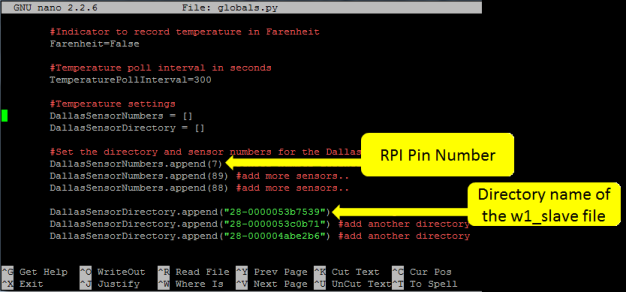
Page down until you see the DallasSensorNumber settings (as per Figure 4). Enter the GPIO number of the sensor (e.g. DallasSensorNumber(7) ), replacing the numbers you see in the file with your own numbers. If you have multiple sensors then repeat the line with the other GPIO numbers (as per Figure 4). Then do the same for the directory name replacing the directory names you see with your directory names that you made a note of in step 1.
If you want your temperature to be display in Fahrenheit instead of Celsius then find the line that says Farenheit=False and change it to Farenheit=True (refer the top two lines of Figure 4).
Press CTRL-X
Then press Y to save the file
Press ENTER
Step 5: Run dallas.py program
pi@raspberrypi / $
Type:
sudo python dallas.py
If you are getting errors or problems see here for diagnostic steps.
Step 6: View your dashboard
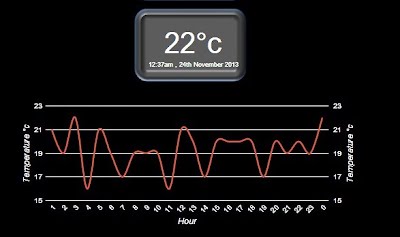
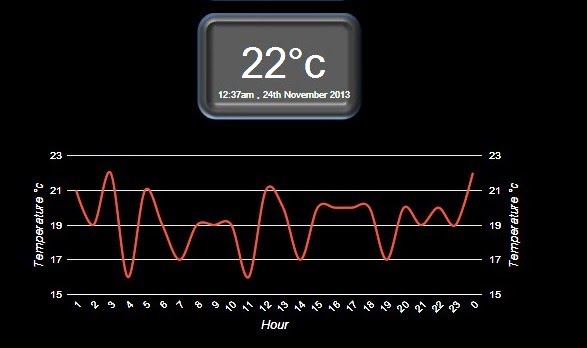
If you want to display a graph then select the 'Display graph on dashboard' option from the Config menu.
|
Home >